If you are new to Laravel and don’t understand what MVC means, don’t worry.
This blog will explain the MVC concept in Laravel in the simplest possible way, even if you have zero programming knowledge.
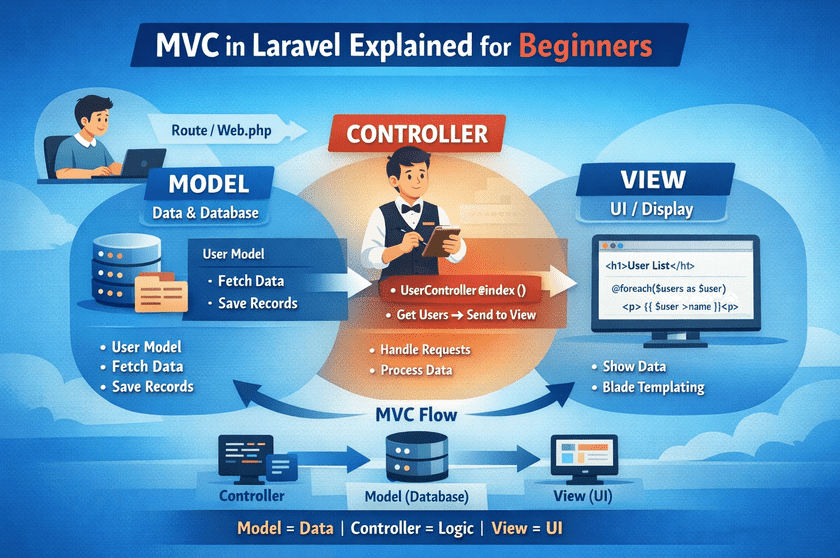
What is MVC?
MVC stands for:
- M – Model
- V – View
- C – Controller
Laravel uses the MVC architecture to organize code properly and make applications easy to understand, manage, and scale.
In simple words:
MVC separates data, logic, and design.
Why MVC is Important in Laravel?
Without MVC, all code becomes messy and difficult to manage.
MVC helps developers by:
- Keeping code clean
- Making debugging easier
- Improving project structure
- Making applications scalable
Laravel follows MVC by default, which is why it is so popular.
Understanding MVC with a Real-Life Example (Restaurant 🍽️)
Think of MVC like a restaurant:
| MVC Part | Restaurant Example |
|---|---|
| Model | Kitchen |
| Controller | Waiter |
| View | Plate / Screen |
Model in Laravel (M)
What is a Model?
The Model handles data and database operations.
It:
- Connects to the database
- Fetches data
- Saves data
- Updates and deletes records
Where is Model Located?
app/Models/Example:
app/Models/User.phpSimple Meaning:
Model knows how data is stored and retrieved from the database.
Controller in Laravel (C)
What is a Controller?
The Controller handles the logic of the application.
It:
- Receives requests from users
- Calls the Model
- Sends data to the View
Where is Controller Located?
app/Http/Controllers/Example:
app/Http/Controllers/UserController.phpSimple Meaning:
Controller decides what should happen when a user makes a request.
View in Laravel (V)
What is a View?
The View is responsible for displaying data to the user.
It:
- Shows HTML content
- Displays data received from the Controller
- Does NOT contain business logic
Where is View Located?
resources/views/Example:
resources/views/users.blade.phpSimple Meaning:
View only shows data on the screen.
How MVC Works in Laravel (Flow)
Here is the complete flow of MVC in Laravel:
User Request
↓
Route
↓
Controller
↓
Model (Database)
↓
Controller
↓
View
↓
Response to User
Simple Laravel MVC Example
Step 1: Route
// routes/web.php
Route::get('/users', [UserController::class, 'index']);👉 When user opens /users, Laravel calls the controller.
Step 2: Controller
use App\Models\User;
class UserController extends Controller
{
public function index()
{
$users = User::all();
return view('users', compact('users'));
}
}
👉 Controller:
- Gets data from the Model
- Sends data to View
Step 3: Model
class User extends Model
{
}👉 Model connects to the users table.
Step 4: View
<h1>User List</h1>
@foreach($users as $user)
<p>{{ $user->name }}</p>
@endforeach
👉 View displays data on the screen.
MVC in One Line (Easy to Remember)
- Model = Data
- Controller = Logic
- View = Design
Common Beginner Mistakes
❌ Writing database code in View
❌ Writing HTML inside Model
❌ Mixing logic everywhere
✔ MVC keeps everything separate and clean
Conclusion
MVC is the backbone of Laravel.
Once you understand MVC, learning Laravel becomes much easier.
If you are a beginner, focus on learning:
- Routes
- Controllers
- Views
- Models